Socket Welding Flanges and Fittings. 62 Design of Welded Connections Fillet welds are most common and used in all structures.
Skewed T Joints Between 60 And 30 Degrees
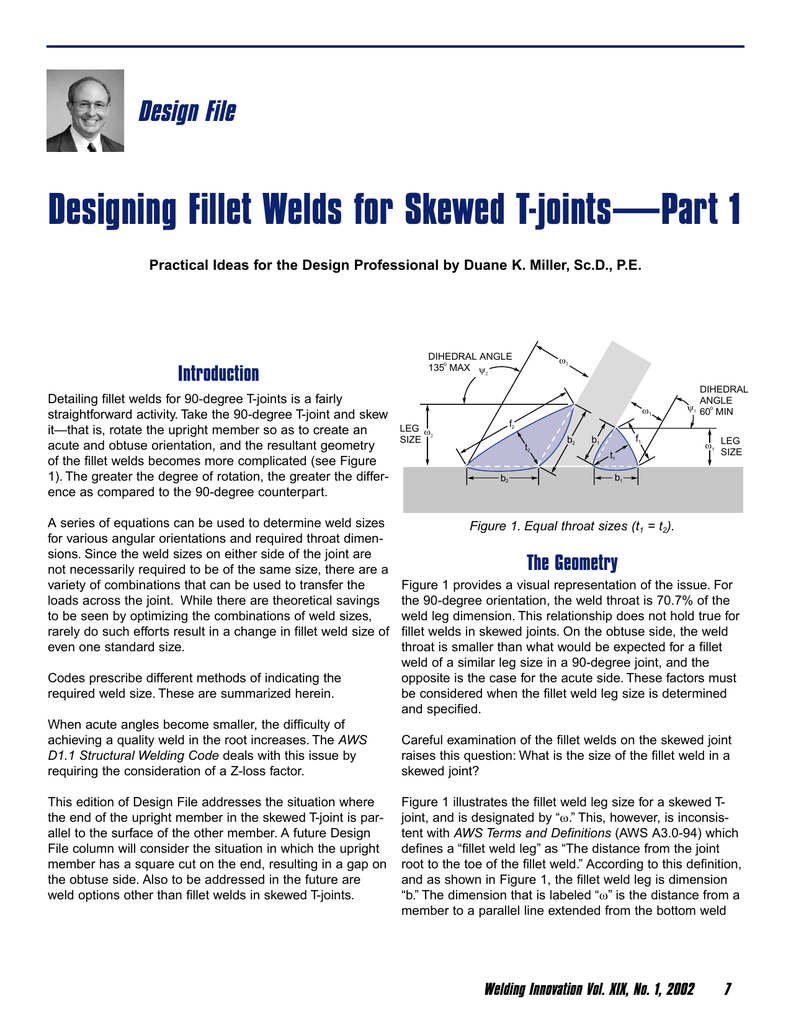
Designing Fillet Welds for Skewed T-Joints Part 1 Lessons Learned in the Field.
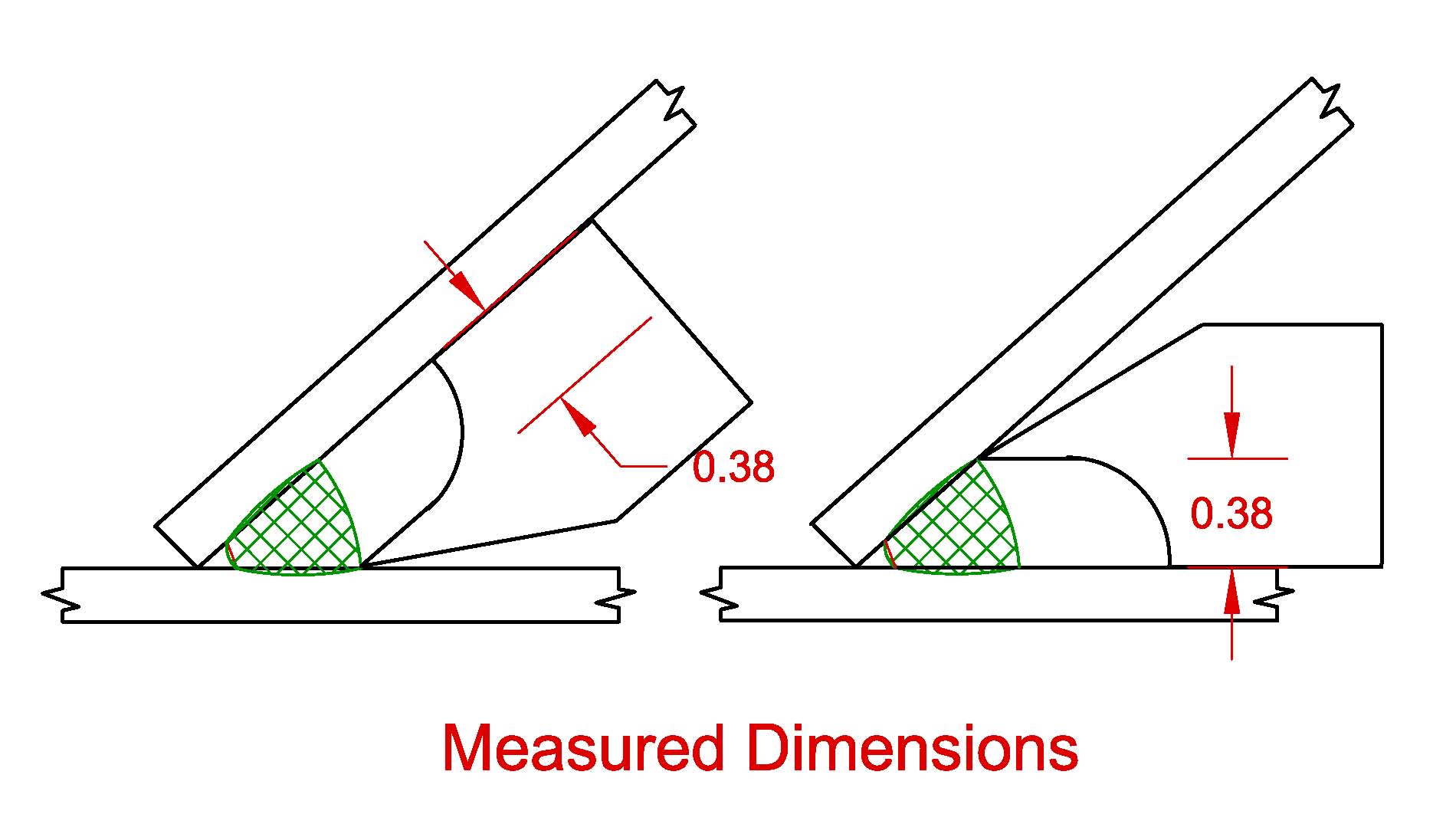
. See Annex II for formula governing the calculation of effective throats for fillet welds in skewed T-joints. A T-joint fillet weld. Skewed T Joints Intersecting Member 135 deg.
Fillet Weld Design for Skewed Shear Tabs Flow Chart 5 16 t p ½ 0 θ 45 Table 10-14C 14th Ed. Part 12013 Manual metal-arc welding gas-shielded metal-arc welding gas weld-ing Written By kendrickbrenner11517 March 31 2022 Add Comment Edit. Part 12013 Manual metal-arc welding gas-shielded metal-arc welding gas weld-ing TIG welding and beam welding of steels.
In calculating tn in the D11 tn defined as the distance from the root of the joint to the face of the diagrammatic weld tn w2sinpsi2. B Corner joint fillet weld. Fillet welds are probably the most common type of weld particularly in structural steelwork applications so this first section will look at some of the design considerations of fillet welds.
Engineers and designers have been alerted to the AISCAWS requirements for limiting angles for skewed T-joints. 24 Fillet Welds 241 Effective Throat 2411 Calculation. There is no specific guidance on which method to use and in practice the choice is usually made on practical grounds.
Types of joint preparation. However it always fails in shear. A T-joint fillet weld.
Per the D11 the equivalent leg size would be 123 x 019 0234 w. Download Citation Designing fillet welds for skewed T-joints - Part 1 Detailing fillet welds for 90-degree T-joints is a straightforward activity. Min1 Theoretical Throat Through Member 1When the intersecting member is less than 60 degrees the weld shall be considered a partial penetration groove weld.
Skewed T-joint fillet welds have either been qualified by analysis andor testing or are considered nonload carrying welds. A weld preparation the weld prep is therefore. Part 21998 Submerged arc welding of steels.
The requirements of 2328 shall apply. 2337 Effective Throat of Skewed T-Joints. They may be used to make T lap and corner joints Fig4.
Consider the Transfer of Stress through Members Welding Innovation Vol. 2336 Minimum Skewed T-Joint Weld Size. The American Welding Society Structural Welding Code - Steel AWS D11 provides design and detailing requirements for skewed t-joints.
Depending on the skewed t-joint geometry designers are required to define the required weld leg or effective throat size. Designing fillet welds for skewed t joints part 2. The skewed T-Joint angle is 120 degrees psi symbol zero root opening.
Increments A fillet weld can be loaded in any direction in shear compression or tension. The effective throat of a skewed T-joint in angles between 60 and 30 shall be the minimum distance from the root to the diagrammatic face. However many designers are unaware of the AWS D11 skewed t-joint requirements and apply typical 90.
In order to weld the full thickness of a plate and achieve the weld throat thickness required by design it is therefore necessary to cut away sufficient metal along the joint line so that the welding electrode has access to the root of the joint enabling the root pass to be deposited and then the remainder filled to complete the joint. Depending on the skewed t. Commonly used in the structural industry T-joints generally use fillet or groove type welds which may be referred to as weld overlays.
A T-joint consists of two plates welded at 90 to each other in the form of a T. The present invention comprises a gauge for measuring certain dimensions of welds at skewed T joints the gauge being broadly denoted by the numeral 10. AiSC Manual Skewed Shear Tab Fillet Welds aiSC 360-10 aWS D11D11M2010 1 2 θ 10 Provide Fillet Weld leg Size Clause 234 aWS a 10 θ 60 Provide Effective Throat area Clause 234 aWS B 60 θ.
Which can be inscribed within the fillet weld cross section. Other references For those who are interested in actually designing welds the following is a useful simple guide. C Lap joint fillet weld.
No reduction shall be assumed in design calculations to allow for the start or stop of the weld. Other welds include partial penetration groove welds. Types of joint preparation.
The effective throat shall be the shortest distance from the joint root to the weld face of the diagrammatic weld see Annex I. The American Welding Society Structural Welding Code - Steel AWS D11 provides design and detailing requirements for skewed t-joints. 2 Skewed T Joints Between 60 And 30 Degrees 2 Designing Fillet Welds For Skewed T Jointsa Part 1 The James F Welding Joints Types Symbols And Pictures Www Materialwelding Com.
Strength equivalent to a 90 degree 316 inch fillet weld. Single-sided fillet welded joint types. In the directional method the force acting on the fillet weld is resolved into components parallel and.
The simplified and the directional methods. Eurocode 1993-1-82005 gives a designer a choice between two methods for the design of fillet welds. A series of equations can be used to.
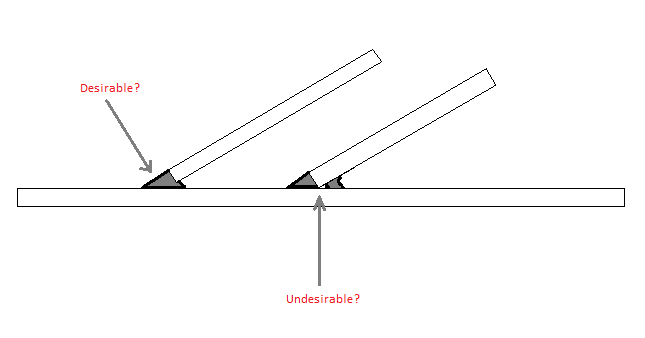
Inspection can be challenging due to the actual weld geometries and the undesirable repetitive echoes within the test piece. They may be used to make T lap and corner joints Fig4. Designing fillet for skewed.
Weld sizes are specified in 116 in. Typical welds capable of being measured with gauge 10 are welds 12 and 14 shown in FIGS. Increments A fillet weld can be loaded in any direction in shear compression or tension.
A tabulation of mea-. Oenoral Construction Specification O-29C has been revised to clarity. Fillet welds are probably the most common type of weld particularly in structural steel work applications so this first section will look at some of the design considerations of fillet welds.

Designing Fillet Welds For Skewed T Jointsa Part 1 The James F


0 comments
Post a Comment